Do Americans Prefer a World Without TikTok?
Summary: A new report from More in Common explores Americans’ attitudes and beliefs around the benefits of social media and support for various government regulations—as well as how they compare to views in the UK, France, and Germany.
In recent years we have seen a growing public concern about the negative effects of social media on society and mental health. In 2016, many left-leaning critics blamed sites such as Facebook and X (formerly Twitter) for enabling disinformation campaigns that skewed the results of the presidential election in favor of Donald Trump. In 2020, similar accusations were made by conservatives, who argued that X and Facebook suppressed information that was unfavorable to Joe Biden.
Meanwhile, scholars have noted an increase in both the average number of daily users of social media over the past decade—from 970 million users in 2010 to 4.95 billion users in October 2023—and the average daily time spent on such sites went from 90 minutes per day in 2012 to 151 minutes per day in 2023 . These trends, when coupled with a troubling increase in mental health issues—particularly among teenagers—have led some to call for increased regulation of such sites for our nation’s young people.
More in Common recently released a report to explore people’s attitudes around the benefits of social media and support for various government regulations. In addition to exploring Americans’ attitudes, we also surveyed people living in France, Germany, and the UK to explore how beliefs compare across these countries.
Below are some of our key findings.
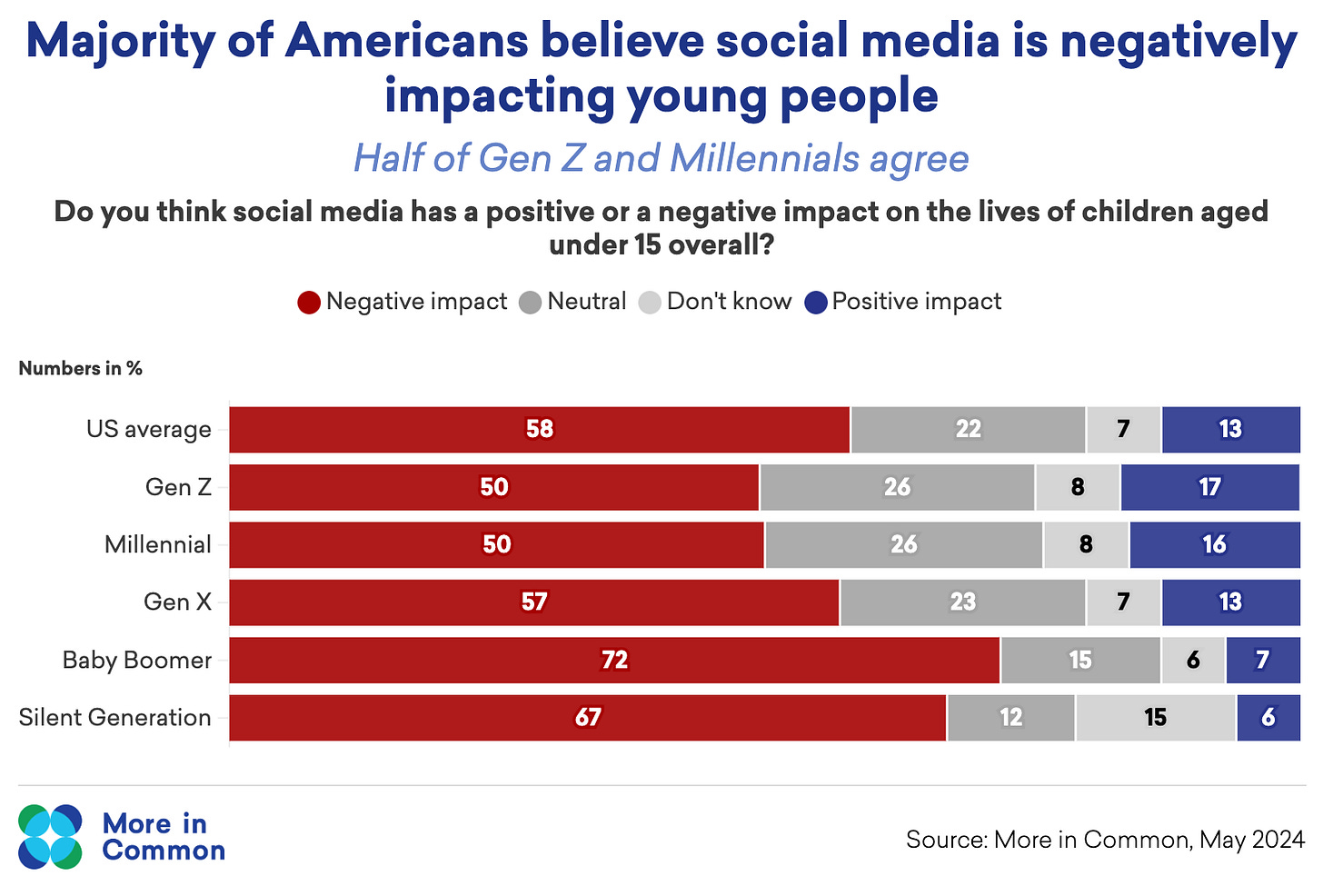
Americans Share a Broad Concern for Social Media’s Impact on Children
Many Americans (58%) are concerned about the negative impacts of social media on children— a concern broadly shared across political parties and generations. A majority of Democrats (56%) and Republicans (61%) think social media has a negative effect on kids, compared to only 15-16% that think it has a positive effect.
Concerns are also shared broadly across generations. Almost three times as many Gen Z Americans believe social media has a negative impact (50%) on children than believe it has a positive impact (17%). Baby Boomers are most likely compared to other generations to believe social media has a negative impact (72%).
Americans Generally Support More Regulations, However Less So than People in Other Countries
There is general bipartisan support among Americans for various regulations that place restrictions on social media and smartphone usage, particularly those that limit access for children.
However, compared to people living in UK, France, and Germany, Americans are least likely to think the government is not doing enough to regulate social media (42%), compared to Germany (51%), France (57%) and the UK (65%).
Americans Have a Complicated Relationship with their Phones
Overall, Americans reported a complicated relationship with their phones. Americans cite many benefits of social media, including providing opportunities to stay in touch with friends (47%), entertainment and fun (32%), and the ability to learn about topics they are interested in (30%). However, most (68%) say they check their phones every 2 hours or less and 50% say they spend too much time on their phone—including 60% of Gen Z.
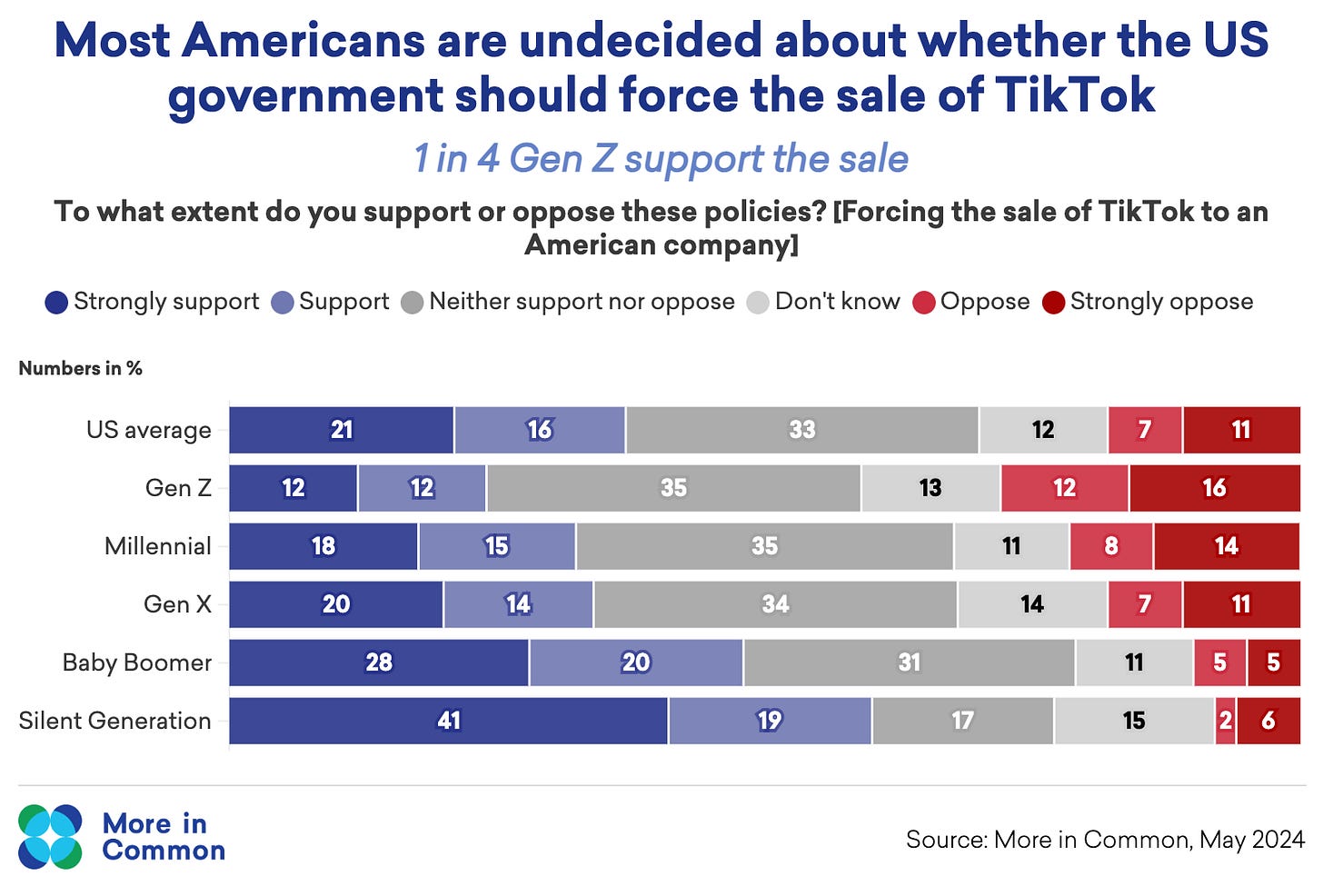
Americans Are Split, Especially Among Generations, on Beliefs Around TikTok
On April 24, President Biden signed into law legislation that would ban TikTok in the US if it is not sold within a year. This has ignited debate within Congress and the American public around the role TikTok plays in American society and its risks to US security. Our research shows that Americans are generally split on views around TikTok and the ban—with views differing generally along generational lines.
For example, only 24% of Gen Z Americans agree with forcing the sale of TikTok to an American company, compared with 48% of Baby Boomers and 60% of Silent Generation Americans.
While 47% of Americans say they would prefer to live in a world where TikTok was never invented, only 34% of Gen Z Americans agree with that statement compared to 70% of Silent Generation Americans.
Conclusion
This research paints a nuanced picture of how Americans are feeling about the effects of social media on their lives, both across demographics and in comparison to other countries. While Americans are more sanguine about the effects of social media than their European counterparts, many remain wary of the possible negative consequences of these platforms in their daily lives. This includes Democrats and Republicans, and even our nation's young people, who demonstrate skepticism about the effects of social media—though less than older Americans. Overall, these observations show increasing public concern regarding the potential risks of these platforms.